Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms and primary food producers that live in both varieties of watery environments, salty and fresh. Bacteria, Protists, and mostly single-celled plants are counted in this category. These microscopic plants are very important to the ocean and to the whole planet.

Phytoplankton consumes carbon dioxide and releases oxygen. Besides that, Plankton makes carbohydrates using light energy. phytoplankton lives near the surface so that enough sunlight can penetrate to power photosynthesis. Many small fishes eat them and then big fishes eat the little fishes. We enter this chain when we eat fish and the energy of phytoplankton becomes our energy. That’s how they take part in the food chain.
The sunlight, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water are used in a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process of making food from plants and phytoplankton. Plankton releases oxygen as waste in this process. Carbon dioxide, iron, nitrogen, and phosphorous are important substances with are required in the procedure.
Where Do Phytoplankton Live
The Word Phytoplankton is derived from the Greek words Phyto (plant) and plankton (made to wander or drift). Phytoplankton are microscopic plants that live in the ocean, seas, or lakes. These small plants are considered very important for the ocean and the earth as they are a very basic and crucial factor in the food chain.

They are single-celled photosynthetic organisms that live under the suspension of water. Like all green plants, phytoplankton have chlorophyll to capture sunlight, and they use photosynthesis to turn it into chemical energy. Phytoplankton lives near the surface of the ocean. Water and nutrients are also needed to create food.
Types Of Phytoplankton
1. Dinoflagellates
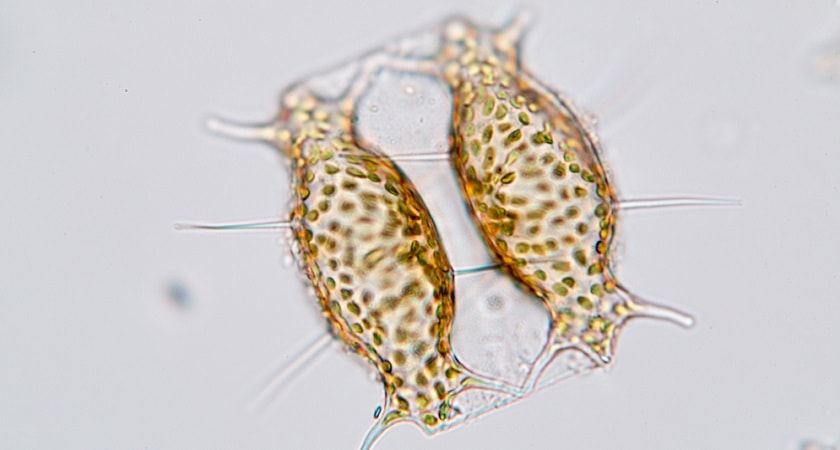
Dinoflagellates are single-celled organisms with two flagella. It is a very common organism in almost every type of aquatic ecosystem. They are prime members of both the phytoplankton and the zooplankton of marine and freshwater ecosystems.
Dinoflagellates are a large group of flagellate eukaryotes that build up the phylum Dinoflagellata. Generally, they are marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Some of them produce toxins that can accumulate in shellfish, resulting in poisoning when eaten.
2. Diatoms
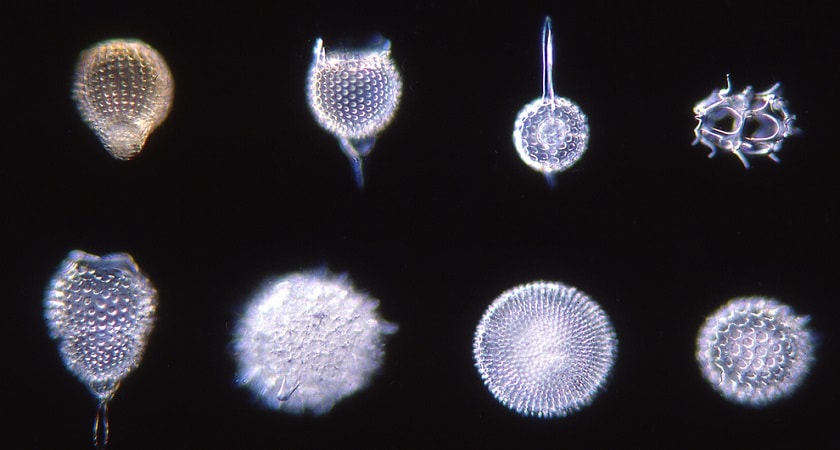
Diatoms are a major group of microalgae that is found in the oceans, waterways, and soils of the world. Also, one of the largest and most significant ecological groups of organisms on Earth is Diatoms.
Because of their unique cell structure, and life cycle, it’s easy to recognize them. It is a single-celled alga that has a transparent cell wall of silica. The size of diatoms ranges typically from a few microns up to about 2 millimeters.
3. Cyanobacteria

Cyanobacteria are a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through photosynthesis and are the only photosynthetic prokaryotes able to produce oxygen. They are also known as “Cyanophyta”. They are aquatic, small, and unicellular and are a great contributor to the origin of plants.
Cyanobacteria are important contributors to nitrogen fertilizer in the cultivation of rice and beans. They are also called “blue-green algae” as they are photosynthetic and aquatic.
4. Coccolithophores
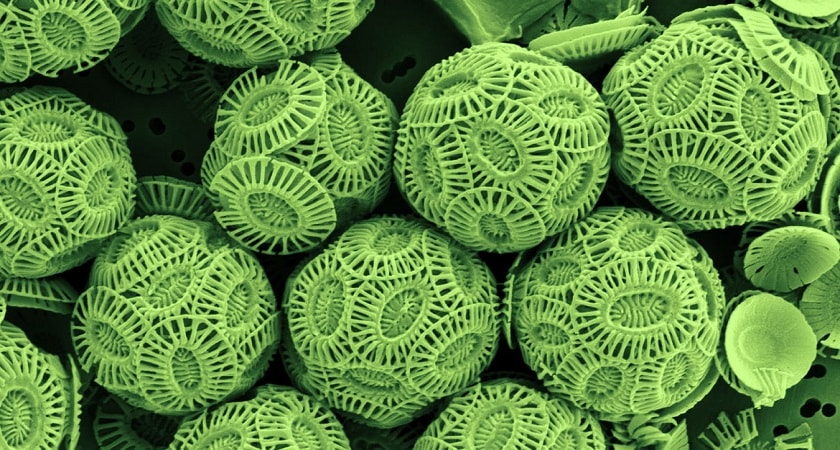

coccolithophore is a unicellular, eukaryotic phytoplankton. They belong either to the kingdom Protista. Like the other phytoplankton, the coccolithophore lives in large numbers throughout the upper layers of the ocean. They surround themselves with microscopic plating made of limestone or calcite.
The scales are known as coccoliths. This plankton is shaped like hubcaps and is only three one-thousandths of a millimeter in diameter. A single coccolithophore is surrounded by at least 30 scales at any one time.
5. Green Plants
All organisms commonly known as green algae, land plants, including liverworts, mosses, ferns, and other non-seed plants, and seed plants are classified and considered in the category of green plants. They are multicellular, predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae.
Importance Of Phytoplankton
- Phytoplankton are tiny photosynthetic organisms and the foundation of the aquatic food web. Although, they are the major producers of marine life, sometimes called the grasses of the sea. Plankton is as important as land plants.
- Phytoplankton produces lots of oxygen through photosynthesis which is the lifeline for the marine species. Especially, they are responsible for half of the photosynthetic activity on Earth, which makes them necessary to both their local and global ecosystems.
- They are a major food source for larger animals. Phytoplankton is at the base of the food chain because these tiny microorganisms produce the first forms of food. Besides that, Zooplankton is another small animal and invertebrates are the primary consumers of phytoplankton. Then Zooplanktons are fed by fish larvae and some small fishes. The large fishes feed on small fishes and then humans consume those big fishes.
- Their importance in controlling carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is noticeable. Along with that, plankton is spread in almost all marine ecosystems and is an autotroph, which forms the foundation of most marine food webs.
- Plankton plays a very crucial role in balancing the climate and the carbon cycle. The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that gets fixed into sugars is because of phytoplankton doing half of the work for the global ecosystem. If phytoplankton is not there, carbon dioxide would continue to be produced in both biological and industrial sources and the level of carbon dioxide would rise consistently.
Plankton is on the food list of every marine species and plays a very crucial role in the global ecology. Let us know what you think about the importance of phytoplankton…Share your thoughts and the information you have about these microorganisms below in the comment section…..
 T-Shirts
T-Shirts Long Sleeves
Long Sleeves Hoodies
Hoodies Sweatshirts
Sweatshirts

 Baby Bodysuits
Baby Bodysuits
 Cap
Cap


In a single – celled organism (Unicellular organism ), one cell carries out all the functions of the body. For example, transporting nutrients, excretion ,etc are performed by the single cell which …
Thanks a lot for sharing this important information with us, hope you liked the article.